Our Blog
10 Simple Workplace, Health & Safety (WHS) tips
These 10 Workplace, Health & Safety (WHS) tips will help you minimise risks and hazards in the workplace. Keep Fire Doors Shut Fire doors must be kept closed at all times (never propped open) if they are to function properly in an emergency. No objects should obstruct fire doors at any time, so if you
Read MoreRoot Cause Analysis During an Accident Investigation
OSHA and EPA Urge Employers to Conduct a Root Cause Analysis OSHA and EPA encourage employers to conduct a root cause analysis following an incident or near miss at a facility. The fact sheet defines a root cause as “a fundamental, underlying, system-related reason why an incident occurred that identifies one or more correctable system failures”. Employers
Read More
Near Miss Reporting as a Leading Indicator
Lagging Indicators and Leading Indicators Used to measure safety performance are Lagging indicators and leading indicators. Whereas the first type of measure is reactive in nature, the second is proactive. Lagging indicators measure facts after they have occurred, such as the number of injuries, lost time from work, etc. As Peter Bussey from LNS Research
Read More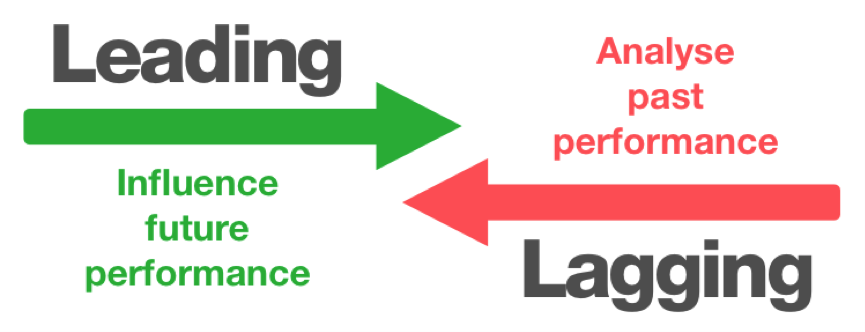
Use Lagging Indicators to Evaluate Leading Indicators
Lagging and Leading Indicators Can Work Together Many safety professionals argue that tracking leading indicators is a more effective way of improving safety performance than lagging indicators. Lagging indicators measure what has already happened (e.g. number of incidents, days away from work), while leading indicators measure proactive, preventative, and predictive initiatives before incidents happen (training,
Read More
Risk Rating for Contractor Work to be Performed
Place Contractors in a Predetermined Risk Category According to the white paper, 9 out of 14 research participants evaluate the risk of the work to be performed by contractors. This is achieved typically through a risk matrix. Contractors are placed in a predetermined risk category, and each risk category may require contractors to take additional steps
Read More
Workplace Inspections – Basic Principles
Workplace inspections help prevent incidents through the critical examination of workplaces. Inspections help identify all types of workplace hazards (biological, chemical, ergonomic, physical), leading to corrective actions. Principles Increase the Effectiveness of Inspections To make workplace inspections as effective as possible, it is helpful to establish and abide by a set of basic principles. The
Read More
3 Different Categories of Leading Indicators
Leading Indicators Are Classified in Three Broad Categories The Campbell Institute at the National Safety Council has published many research reports on leading indicators. One of them, Practical Guide to Leading Indicators: Metrics, Case Studies & Strategies, includes a matrix of key leading indicators, their definitions and associated metrics. The matrix represents a collaborative benchmarking effort
Read More
Controls Methods & Development of a PPE Program
PPE Is the Least Effective Hazard Control Method PPE is worn by workers to minimize exposure to occupational hazards that can cause risks of injury and illness. Examples of PPE include gloves, respirators, safety glasses, full body suits, hard hats, fall protection, aprons, vests, earplugs or muffs, and shoes. Many workplaces will include situations where the
Read More
Review Risk Assessments Periodically
What is a Risk Assessment? In the context of occupational safety and health, a risk assessment is a process that aims to protect workers by preventing injuries and illnesses. A risk assessment includes many specific steps, but they can all be grouped in the following three general steps: 1) Hazard Identification (i.e. what would cause risks of injuries
Read More
Job Hazard Analysis & Job Safety Analysis Review
A Job Hazard Analysis takes a job and breaks it down into individual job steps (or tasks). Hazards are then identified for each job step, followed by the measures required to eliminate or reduce those hazards. Review a JHA/JSA to Keep It Current In its Job Hazard Analysis booklet, OSHA reminds us that reviewing periodically a JHA/JSA ensures
Read MoreCategories
- Our Blog (19)
- Uncategorized (3)