categories Archives » Tundra Safety
10 Simple Workplace, Health & Safety (WHS) tips
These 10 Workplace, Health & Safety (WHS) tips will help you minimise risks and hazards in the workplace. Keep Fire Doors Shut Fire doors must be kept closed at all times (never propped open) if they are to function properly in an emergency. No objects should obstruct fire doors at any time, so if you
Read MoreRoot Cause Analysis During an Accident Investigation
OSHA and EPA Urge Employers to Conduct a Root Cause Analysis OSHA and EPA encourage employers to conduct a root cause analysis following an incident or near miss at a facility. The fact sheet defines a root cause as “a fundamental, underlying, system-related reason why an incident occurred that identifies one or more correctable system failures”. Employers
Read More
3 Different Categories of Leading Indicators
Leading Indicators Are Classified in Three Broad Categories The Campbell Institute at the National Safety Council has published many research reports on leading indicators. One of them, Practical Guide to Leading Indicators: Metrics, Case Studies & Strategies, includes a matrix of key leading indicators, their definitions and associated metrics. The matrix represents a collaborative benchmarking effort
Read More
Controls Methods & Development of a PPE Program
PPE Is the Least Effective Hazard Control Method PPE is worn by workers to minimize exposure to occupational hazards that can cause risks of injury and illness. Examples of PPE include gloves, respirators, safety glasses, full body suits, hard hats, fall protection, aprons, vests, earplugs or muffs, and shoes. Many workplaces will include situations where the
Read More
Review Risk Assessments Periodically
What is a Risk Assessment? In the context of occupational safety and health, a risk assessment is a process that aims to protect workers by preventing injuries and illnesses. A risk assessment includes many specific steps, but they can all be grouped in the following three general steps: 1) Hazard Identification (i.e. what would cause risks of injuries
Read More
Job Hazard Analysis & Job Safety Analysis Review
A Job Hazard Analysis takes a job and breaks it down into individual job steps (or tasks). Hazards are then identified for each job step, followed by the measures required to eliminate or reduce those hazards. Review a JHA/JSA to Keep It Current In its Job Hazard Analysis booklet, OSHA reminds us that reviewing periodically a JHA/JSA ensures
Read More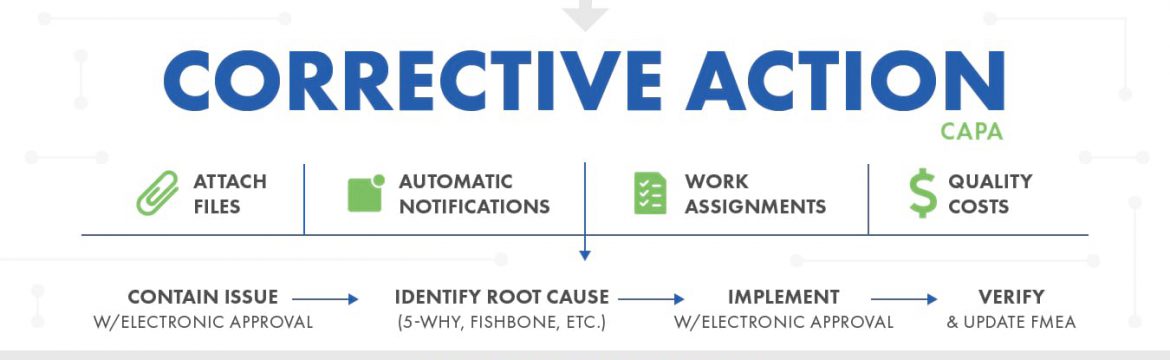
Corrective Actions that Address Root Causes
The Implementation of Corrective Actions Is the Last Step OSHA’s “Incident [Accident] Investigations: A Guide for Employers” document helps organizations implement an incident investigation system composed of the following four steps: 1) Preserve/document the scene2) Collect information3) Determine root causes4) Implement corrective actions According to OSHA’s guidance document, an incident investigation should only be considered complete
Read MoreLaunch Action Plans from Hazard Analysis
Complete Inspections Anywhere & Anytime with Mobility EHS programs include inspections that help to identify workplace hazards that can lead to incidents. In addition to identifying hazards, workplace inspections also help to uncover process weaknesses, which leads to opportunities to improve operational efficiency. A comprehensive inspection program includes both general and special inspections. General inspections are
Read MoreCorrelate Observations with Incident Rates
Use Observations of Unsafe Behaviors as a Leading Indicator To know if you’re doing well, don’t look where you are. Look instead where you’re going. Even if your personal health indicators are good, it doesn’t mean that you’re doing well if you started to eat poorly or sleep less. The same applies to occupational safety.
Read MoreTrain Workers on the Hierarchy of Controls
Train Workers on Hazard Identification and Controls An occupational safety and health (OSH) program also includes training where workers learn more about the OSH program and their responsibilities under it. The training program educates about safety concepts, procedures to follow, how workers can perform their jobs in a safe manner, how to report incidents, and
Read More